

application/vnd.ims.lis.v2.result+json format| Media Type | application/vnd.ims.lis.v2.result+json |
|---|---|
| RDF Type | http://purl.imsglobal.org/vocab/lis/v2/outcomes#Result |
| JSON-LD | http://purl.imsglobal.org/ctx/lis/v2/Result |
IPR and Distribution Notices
Recipients of this document are requested to submit, with their comments, notification of any relevant patent claims or other intellectual property rights of which they may be aware that might be infringed by any implementation of the specification set forth in this document, and to provide supporting documentation.
IMS takes no
position regarding the validity or scope of any intellectual property or other
rights that might be claimed to pertain to the implementation or use of the
technology described in this document or the extent to which any license under
such rights might or might not be available; neither does it represent that it
has made any effort to identify any such rights. Information on IMS's
procedures with respect to rights in IMS specifications can be found at the IMS
Intellectual Property Rights web page: http://www.imsglobal.org/ipr/
Copyright © 2016 IMS Global Learning Consortium. All Rights Reserved.
Use of this
specification to develop products or services is governed by the license with
IMS found on the IMS website: http://www.imsglobal.org/
Permission is granted to all parties to use excerpts from this document as needed in producing requests for proposals.
The limited permissions granted above are perpetual and will not be revoked by IMS or its successors or assigns.
THIS SPECIFICATION IS BEING OFFERED WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY WHATSOEVER, AND IN PARTICULAR, ANY WARRANTY OF NONINFRINGEMENT IS EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMED. ANY USE OF THIS SPECIFICATION SHALL BE MADE ENTIRELY AT THE IMPLEMENTER'S OWN RISK, AND NEITHER THE CONSORTIUM, NOR ANY OF ITS MEMBERS OR SUBMITTERS, SHALL HAVE ANY LIABILITY WHATSOEVER TO ANY IMPLEMENTER OR THIRD PARTY FOR ANY DAMAGES OF ANY NATURE WHATSOEVER, DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY, ARISING FROM THE USE OF THIS SPECIFICATION.
© 2016 IMS Global Learning Consortium, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
The IMS Logo and Learning Tools Interoperability (LTI) are trademarks of the IMS Global
Learning Consortium, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
Figure 1 shows the representation of a Result resource in the application/vnd.ims.lis.v2.result+json format.
{
"@context" : "http://purl.imsglobal.org/ctx/lis/v2/Result",
"@type" : "Result",
"resultScore" : 0.83,
"comment" : "This is exceptional work."
}
This specification defines the structure of a JSON document using a graphical notation. In this notatation, an object is represented by a box that branches out to other boxes corresponding to the properties of that object, as shown in Figure 2.
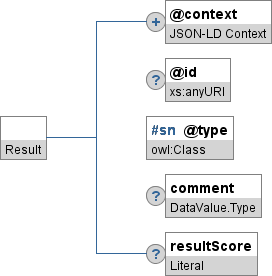
Each box representing a property specifies the name and type of the property , as shown in Figure 3.

If a property is optional, its box will be decorated with a circle that contains a question mark, as shown in Figure 3.
An object within a JSON-LD document may have one of four possible representations:
When an object or enumerable value is to be identified by a simple name, the box representing the corresponding property will be decorated with the #sn hash tag, as shown in Figure 4.

The JSON-LD standard reserves a handful of property names and tokens that have special meaning. These names and tokens, described below, begin with the '@' symbol.
The @id property may identify a so-called blank node by using a CURIE with an underscore as the prefix. The binding of a JSON-LD document MAY include identifiers for blank nodes, but these identifiers are not required.
JSON-LD specifies four other reserved terms (@value, @language, @container, @list). Ordinarily, these terms are not used in the JSON binding for Result objects. However, implementations that extend this specification by including additional properties may utilize these reserved terms in accordance with the rules defined by [JSON-LD-syntax].
In JSON-LD, a context is used to map simple names that appear in a JSON document to URI values for properties or data types in a formal vocabulary (typically an RDF ontology).
The following list defines the necessary and sufficient conditions for a document to conform to the application/vnd.ims.lis.v2.result+json media type.
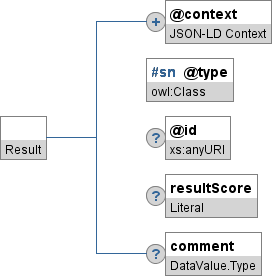
@type property whose value is "Result".@context property that references one or more JSON-LD contexts (either by URI or by value).@context property, a non-empty collection MUST always be represented as a JSON array whose values are enclosed in square brackets. Whereas, in general, the JSON-LD syntax specification allows a collection containing a single value to omit the square brackets, the application/vnd.ims.lis.v2.result+json media type requires square brackets for all non-empty collections other than the @context property.@id property of a given object is mandatory if the minimum cardinality of that property, as defined by this specification, is greater than zero. The @id property is optional for all other objects (even if it is not explicitly listed in the set of properties for an object). Conforming implementations SHOULD include the @id property for all addressable objects.@id property is mandatory, then the value MUST NOT treat the object as a blank node. In this case, the @id value MUST NOT be a CURIE with an underscore as the prefix.@type property and a @context property.@type property if the object value is a subtype of the declared range of the property.Figure 5 presents a complete graphical representation of the JSON binding for a Result object. The subsections following this figure provide details about each object that appears in the JSON binding for a Result object.
{
"@context" : "http://purl.imsglobal.org/ctx/lis/v2/Result",
"@type" : "Result",
"resultScore" : 0.83,
"comment" : "This is exceptional work."
}

| Property | Mult | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| @context | 1..* | This value specifies one or more JSON-LD contexts, either by reference or by value. When multiple contexts are specified, they must be encapsulated within an array. For most implementations, the value will be the single URI for the standard context associated with the |
JSON-LD Context |
| @type | 1 | A simple name identifying the object's type. The standard context [LIS-v2-Result] defines the following simple names that are applicable:
Implementations may use a custom JSON-LD context which defines simple names for additional types that are subtypes of |
owl:Class (Simple Name reference)
|
| @id | 0..1 | The URI that identifies this Result instance. |
xs:anyURI |
| resultScore | 0..1 | The final score that should be displayed in a gradebook for this Result object. | Literal |
| comment | 0..1 | A comment about this Result suitable for display to the learner. Typically, this is a comment made by the instructor or grader. | DataValue.Type |
| Restriction Base | http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string |
|---|---|
| maxLength | 4096 |
| Restriction Base | http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string |
|---|
| Title: | Result JSON Binding in the application/vnd.ims.lis.v2.result+json format |
|---|---|
| Editor: | Stephen Vickers (IMS Global) |
| Version: | 2.0 |
| Version Date: | 10 September 2015 |
| Release: | Final Release |
| Status: | IMS Final Release |
| Purpose: | This document is made available for review and comment by the public community at large. |
The following list of individuals contributed to the authoring of this document:
| Craig Dunk | D2L | Padraig O'hiceadha | HMH |
| Viktor Haag | D2L | Charles Severance | IMS Global |
| Brad Humphrey | Instructure | Colin Smythe | IMS Global |
| Greg McFall | Pearson | Matt Stoelting | Cengage |
| Mark McKell | IMS Global | John Tibbetts | Vitalsource |
| Bracken Mosbacker | Lumen Learning | Claude Vervoort | Cengage |
| Lance Neumann | Blackboard | Stephen Vickers | IMS Global |